Geosynthetics, as synthetic materials, plays a critical role in contemporary geotechnical engineering and construction practices. Derived from polymeric materials, These engineered materials are designed to improve the performance, durability, and functionality of soil and rock structures. Geosynthetics are widely used in various civil engineering applications, including roads, railways, embankments, retaining walls, landfills, ponds, erosion control, and environmental protection.
The primary objective of this article is to provide an introduction to geosynthetics, covering their materials, the different types, functions, benefits and applications of geosynthetics. By delving into these aspects, readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter.
1. What Are Geosynthetics Made Of?
Geosynthetics are commonly manufactured using a variety of polymers, with high-density polyethylene (HDPE), polypropylene (PP), and polyester (PET) being the most popular choices. These polymers are selected for their exceptional resistance to chemical and biological degradation. To enhance specific properties like weathering resistance and UV resistance, manufacturers often introduce additives or modifiers into the polymer blend. In certain specialized applications demanding extraordinary strength, polymers such as aramids or polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) may be utilized. Following is the introduction of these three main materials.
High Density Polyethylene (HDPE): Polyethylene-based geosynthetics exhibit good flexibility, impact resistance, and chemical resistance. They are used in applications such as geomembranes, geotextiles, and geocells for containment, drainage, and erosion control.
Polypropylene (PP): Polypropylene-based geosynthetics are known for their high tensile strength, durability, and resistance to chemical and biological degradation. They are widely used in applications such as geotextiles, geogrids, and erosion control products.
Polyester (PET): Polyester-based geosynthetics offer excellent strength, dimensional stability, and resistance to UV radiation. They are commonly used in geotextiles, geogrids, and geocomposites for reinforcement, separation, and filtration purposes.
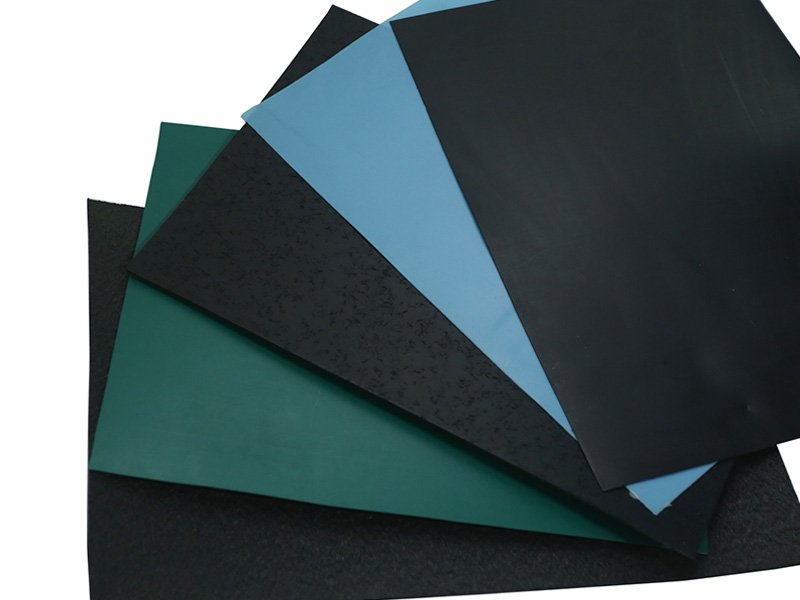



2. What Are Of Geosynthetics Types?
At The Best Project Material Co. Ltd, we offer eight types of geosynthetics, each designed and manufactured with specific characteristics and applications in mind. These geosynthetics can be categorized as follows:
2.1 Geomembranes
Geomembranes are often included as the impermeable part of the engineered barrier system for modern projects, which is widely used across a variety of industries including waste, water, aquaculture, mining, power plant, industrial and civil engineering, etc. BPM brand geomembrane products are made of finest quality high-density polyethylene (HDPE) with specially formulated, virgin polyethylene resin by the state of the art automatic production lines and advanced pressing. Our geomembrane products include Smooth Geomembrane HDPE Liner, Textured HDPE Geomembrane and Composite Geomembrane Liner, etc.
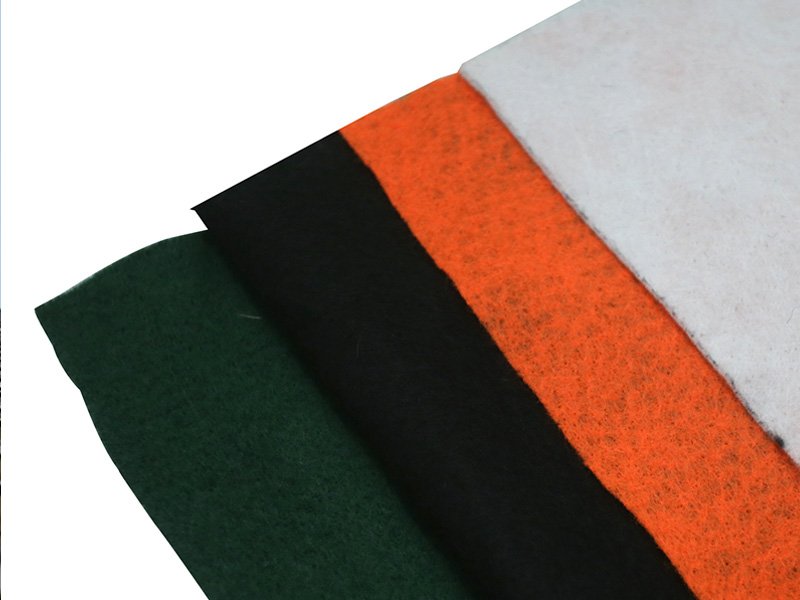
2.2 Geotextiles
Geotextiles are the largest group of geosynthetics, as well as one of the earliest types to be created. Geotextile is made from synthetic fibers, Polypropylene (PP) and Polyester (PET), and can be created as either woven, knitted or non-woven textiles. The non-woven types are manufactured from directionally or randomly oriented fibres/filaments mechanically or thermally/chemically bonded together. They can vary in strength and weight, from lightweight filter products to high strength reinforcement materials.
2.3 Geogrid
Geogrids are high-strength mesh-like structures made from polymers or metals. They provide soil reinforcement and stabilization by improving the load-bearing capacity of the soil. Geogrids are commonly used in retaining walls, slopes, embankments, and road construction projects. They distribute the applied loads and reduce lateral movement, enhancing the stability and longevity of the structures.
2.4 Geocomposites
Geocomposites are composite materials that combine two or more geosynthetic components. These components can include geotextiles, geogrids, geomembranes, or other specialized materials. Geocomposites are designed to perform specific functions such as filtration, drainage, reinforcement, or protection. They offer enhanced performance and versatility compared to individual geosynthetics. Examples of geocomposites include geotextile-geonet composites and geotextile-geomembrane composites.
2.5 Geosynthetic Clay Liners (GCLs)
Geosynthetic Clay Liners consist of a layer of bentonite clay sandwiched between geotextiles. They provide a combination of hydraulic barrier properties and reinforcement. GCLs are commonly used in landfill liners, containment systems, and environmental sealing applications. The bentonite clay swells when it comes into contact with water, forming an impermeable barrier that prevents the migration of liquids or gases.
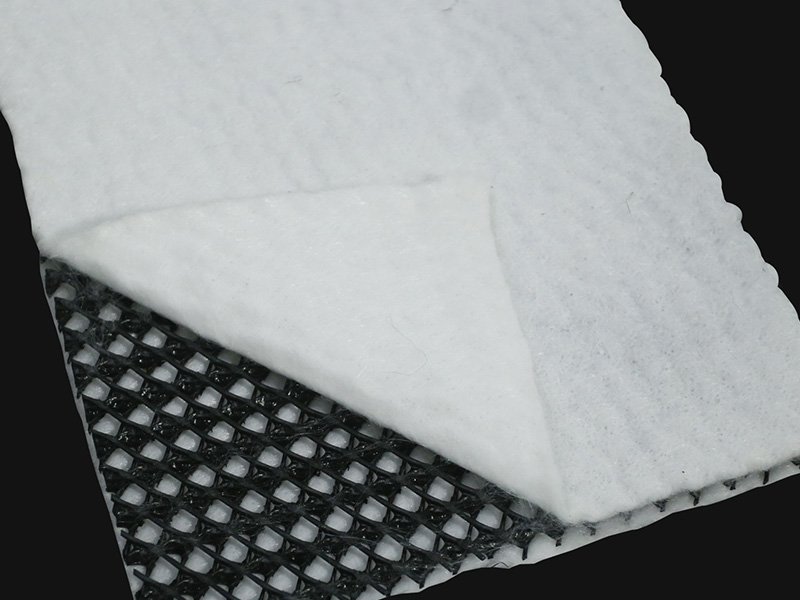
2.6 Geonets
Geonets are geosynthetic material consisting of integrally connected parallel sets of ribs overlying similar sets at various angles for in-plane drainage of liquids or gases. Geonets are often laminated with geotextiles on one or both surfaces and are then referred to as drainage geocomposites.
2.7 Geocells
Geocells are the cost effective geosythetic products which are widely used in construction for erosion control, soil stabilization on flat ground, shorelines, steep slopes, multi-layered retaining walls, channel protection and structural reinforcement for heavy duty load support roads and earth retention.
2.8 Geomat Fabric
HDPE geomat fabric is a new type of geosynthetic material with three-dimensional structure suitable for soil and water conservation, which can effectively prevent soil and water loss, increase green area, and improve the ecological environment.
3. What Are Benefits of Geosynthetics?
Geosynthetics offer several benefits in various civil engineering and construction applications. Some of the key advantages of geosynthetics include:
3.1 Reinforcement
Geosynthetics provide enhanced strength and stability to soil structures, improving load-bearing capacity and preventing soil erosion. They can reinforce embankments, retaining walls, slopes, and foundations, increasing their overall performance and longevity.
3.2 Separation
Geosynthetics act as a barrier between different soil layers, preventing intermixing and maintaining their integrity. This separation function helps to enhance the stability and functionality of structures, such as roads, railways, and landfill liners.
3.3 Filtration and Drainage
Geosynthetics allow for the efficient passage of water while preventing the migration of fine particles. They facilitate proper drainage, preventing the buildup of excess pore pressure and reducing the risk of soil instability or failure.
3.4 Erosion Control
Geosynthetics can effectively control erosion by stabilizing soil surfaces and preventing surface water runoff. They are used in erosion control blankets, geocells, and geotextiles to protect slopes, riverbanks, and shorelines from erosion caused by water or wind.
3.5 Environmental Protection
Geosynthetics play a crucial role in environmental preservation. They are used in landfill liners and caps, preventing the migration of contaminants into the surrounding soil and groundwater. Additionally, they help in the construction of erosion control measures and restoration of damaged ecosystems.3.6
3.6 Cost-Effectiveness
Geosynthetics offer cost advantages by reducing the need for traditional construction materials and labor-intensive methods. They can simplify construction processes, accelerate project timelines, and provide long-term cost savings through improved performance and reduced maintenance requirements.
3.7 Sustainability
Geosynthetics contribute to sustainable engineering practices by promoting resource conservation and minimizing environmental impacts. They can be made from recycled materials and are often designed for durability, reducing the need for frequent replacements.


4. How Do Geosynthetics Work?
Geosynthetics have diverse applications in geotechnical engineering and construction projects. Here are some common examples:
4.1 Roads and Highways
Geosynthetics are used in road and highway construction to improve pavement performance, reinforce weak soils, separate different soil layers, and enhance drainage systems. They help in reducing rutting, cracking, and pavement deformation, resulting in longer-lasting and more durable road infrastructure.
4.2 Retaining Walls and Slopes
Geosynthetics provide reinforcement and stabilization to retaining walls and slopes, preventing soil erosion and movement. They increase the load-bearing capacity of the soil, reduce lateral pressures, and enhance overall stability. Geogrids and geotextiles are commonly used in these applications.
4.3 Landfills and Waste Containment
Geomembranes and geosynthetic clay liners (GCLs) are extensively used in landfill liners and caps to prevent the migration of contaminants into the environment. Geomembranes act as impermeable barriers, while GCLs provide a combination of hydraulic barrier properties and reinforcement.
4.4 Water and Wastewater Management
Geomembranes and geotextiles are used in the construction of ponds, reservoirs, and water containment structures. They prevent seepage, control water levels, and ensure proper containment for water supply, irrigation, and wastewater treatment facilities.
4.5 Erosion Control and Coastal Protection
Geosynthetics play a vital role in erosion control measures, such as erosion control blankets and geotextiles. They stabilize soil surfaces, prevent erosion, and protect coastlines, riverbanks, and slopes from the forces of water flow.
4.6 Environmental Remediation
Geosynthetics are used in environmental remediation projects to contain and isolate contaminated sites. They provide barriers to prevent the migration of pollutants and facilitate the proper management and cleanup of hazardous materials.
4.7 Mining and Energy Industry
Geosynthetics find applications in the mining and energy sectors, including heap leach pads, tailings dams, and containment systems for oil and gas exploration. They provide impermeable barriers, reinforcement, and erosion control measures to ensure safe and sustainable operations.
5. Conclusion
Geosynthetics have revolutionized geotechnical engineering and construction practices, offering numerous benefits and improved performance in a wide range of applications. From road construction and retaining walls to landfill liners and erosion control, geosynthetics provide stability, drainage, reinforcement, and environmental protection. By utilizing geosynthetics effectively, engineers and construction professionals can enhance the longevity, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness of their projects. As technology advances, geosynthetics continue to evolve, offering innovative solutions for the challenges faced in the geotechnical and construction industry.





